Basic description
Apache airflow is a platform for authoring, scheduling and monitoring workflows. It is useful in architecting and orchestrating data pipelines. You can think of it like an upgrade on cron jobs. All workflows are represented as Directed Acyclic Graphs(DAGs) which can be thought of as a collection of tasks.
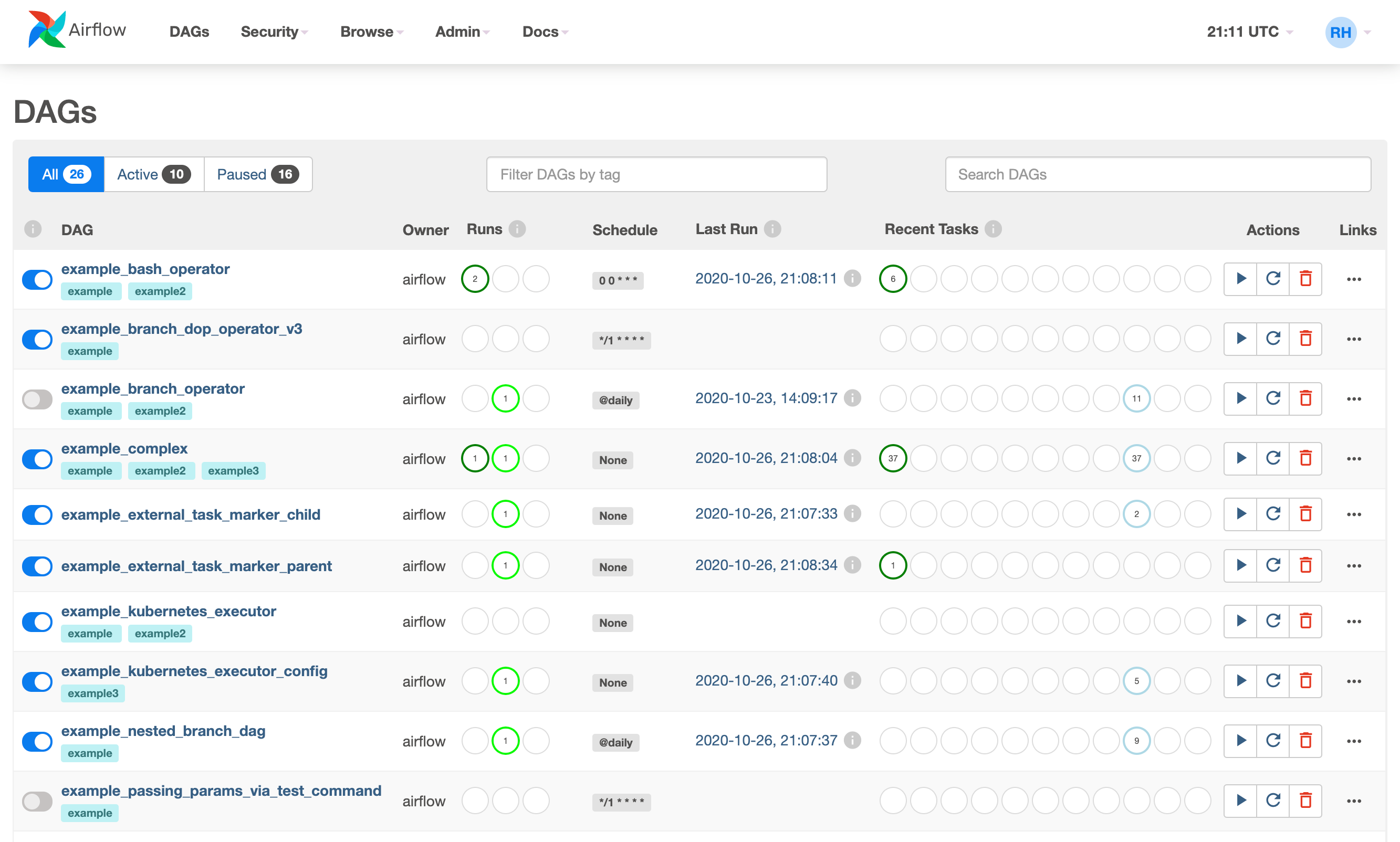 Basic interface for ariflow this is useful for monitoring and testing dags
Basic interface for ariflow this is useful for monitoring and testing dags
Airflow DAGs concept:
A created DAG would specify the dependecies between Tasks, and the order of their execution, and number retries that should happen. A task represents each node of a DAG and the actual work done each task represents is defined by operators. A task can be created for fetching data, running analysis, triggering other systems, or more. So basic characteristics of a DAG are:
- Directed: each task must have at least one defined upstream or downstream task.
- Acyclic: This means that no single task should point back to itself as we don’t want to create infinite loops.
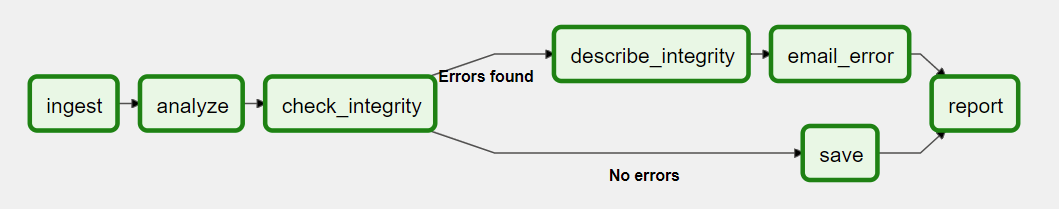 An Image of a basic Dag
An Image of a basic Dag
Control Flow
As the case with regular pipelines, Dags are designed such that they can be run multiple times. They can also be parameterised. Since a Dag is usually a collection of several tasks, these tasks have dependencies declared on each other. You’ll see this in a DAG either using the » and « operators.
Operators:
They define what a particular task should do. There are 3 main operators:
- Action operators: they execute a function eg PythonOperator or BashOperator
- Transfer operators: move data between different sources
- Sensor Operators: they wait for something to happen.
Hierarchical view:
DAG
- Operator
- Task
- Operator
- Task
Basic python script
All Dags are created using python code and below is an example of a basic script:
"""
Example DAG
"""
from datetime import datetime
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.dummy import DummyOperator
from airflow.utils.edgemodifier import Label
with DAG(
"example_branch_labels"
, schedule_interval="@daily"
, start_date=datetime(2021, 1, 1)
, catchup=False
) as dag:
ingest = DummyOperator(task_id="ingest")
transform = DummyOperator(task_id="transform")
load = DummyOperator(task_id="load")
ingest >> transform >> load
if __name__ == "__main__":
dag.cli()